As the world evolves, so does the needs of humanity. Long ago, a simple living could already suffice in growing a family, but now with developed and developing economies, it is entirely different. Since the emergence of science some 3000 years ago, several tools humans need require electricity to make them work. Everything that we have in the comforts of our home is powered and generated by electricity, which makes it a part of the basic needs in the modern world.
Power Outages

Just a few hours of a power outage can already ruin almost a whole day’s plans because we cannot go on with our work. Imagine experiencing a total power shut down for at least 48 hours. Imagine the horror and sense of worriedness creeping in the dark because there is no electricity. People in Texas can relate to this. However, that is not only the problem.
Texas Power Crisis
As per research, people in the community experience almost 0 signal receptions, rampant articles about companies skipping about $2.5 billion charges from February, and at least a third of the state’s experience total power outage. Texas could be one of the most popular states per record for the first three months of 2021. The reason for the popularity is the Texas Power Crisis, total power outages, which brought too much disarray amongst its populace.

The known power crisis was caused by a historical winter storm named Uri. Its aberrant cold temperature waltzing in the state knocked out at least a third of Texas’ power generating capacity. What an excellent way to start, yet another month, with the pandemic still at its high peak.
Now, several people would like to label this as ‘The Great Texas Blackout’ as the issue grew widely because, ironically, Texas is the energy capital of the world. (Cong, et.al, 2021). According to Time Magazine, this issue resulted in being the largest forced blackout in the history of the US. A lingering question about how on earth did the state experience such a dilemma?
How did the Texas Power Crisis happen?
Without overpassing the current issue of the state, few notable countries, such as Canada, Sweden, and American Midwest, also faced harsh weather conditions. Yet, a resolution would always rise to solve the problem. We can definitely understand the clamor and frustrations people in Texas experience. People who are living in Texas experienced not just power outages but also water shortages for 48 hours. Texans had to resort to boiling tap water before drinking it because it may be unsafe to drink without boiling it.
“Water pressure is very low. Please do not run water to keep pipes from bursting,” Houston Mayor Sylvester Turner said on Twitter.
The local newspaper, Texas Tribune, reports, “Approximately 590 public water systems in 141 Texas counties have reported disruptions in service, affecting 11.8 million people as of late Wednesday afternoon, according to a Texas Commission on Environmental Quality spokesperson.”

Consequently, about 2.7 million households are experiencing a loss of power. Moreover, as the temperature drops, the more it gets hard for these people as they have no other materials to keep them extra warm. Suggesting that fireplace inside their homes and fur coats can no longer suffice the cold temperature Winter Strom Uri gives off.
The worse part of this all is reports flying above the state saying that there would be more power outages that the state will experience. Hence, the struggle of keeping warm would still go on. In line with this, frozen wind turbines are not the leading cause of these power outages. Hence, classes now transition to remote learning as pandemic heightens and power crises occur.
On the brighter side, despite millions of Texans experience a power crisis, not all areas in Texas experienced this. As they say, Texas is the known energy capital in the world for the grounds. Unlike other states and countries with interconnected power setups, Texas has its power grid. “That grid, which operates as the Electric Reliability Council of Texas, covers 90% of the state. The other 10% includes El Paso, the upper Panhandle and a chunk of East Texas”. (Aguilar & Limon, 2021).
The said grid began during WWII because of the war needing an ample power supply along Texas’ Gulf Coast. El Paso, as per research, has initially been local, but it began thriving to look for other resources. “Then, in the late 1970s, El Paso Electric became part owner of the Palo Verde Nuclear Generating Station in Arizona.” (Aguilar & Limon, 2021). Thanks to El Paso Electric connected to southern New Mexico, 10% of the population in Texas has their lights on amidst the 90% experiencing a power outage.
Factors behind the Texas Power Crisis
A wide issue like this is not an exemption for pin-pointing fingers of the community and those in authority. “The main cause of the massive disruption, by far, were the frozen components leading to the outage of thermal plants that heat water and convert the steam to electricity.” (Henson, 2021). Texas Attorney General investigates the power grid operator, the Electric Reliability Council of Texas, because of the power outage and other related concerns.
“They have left 3+ million homes w/o power for days, including my own,” Paxton tweeted. ERCOT is a nonprofit government agency that manages power distributions along with Texas. However, it does not provide electricity for the whole of Texas, but it covers about 75% of the state’s land area and 90% of the residents. (Wendorf, 2021). El Paso is one of the cities that is not under ERCOT, so lights are kept on in the said city.
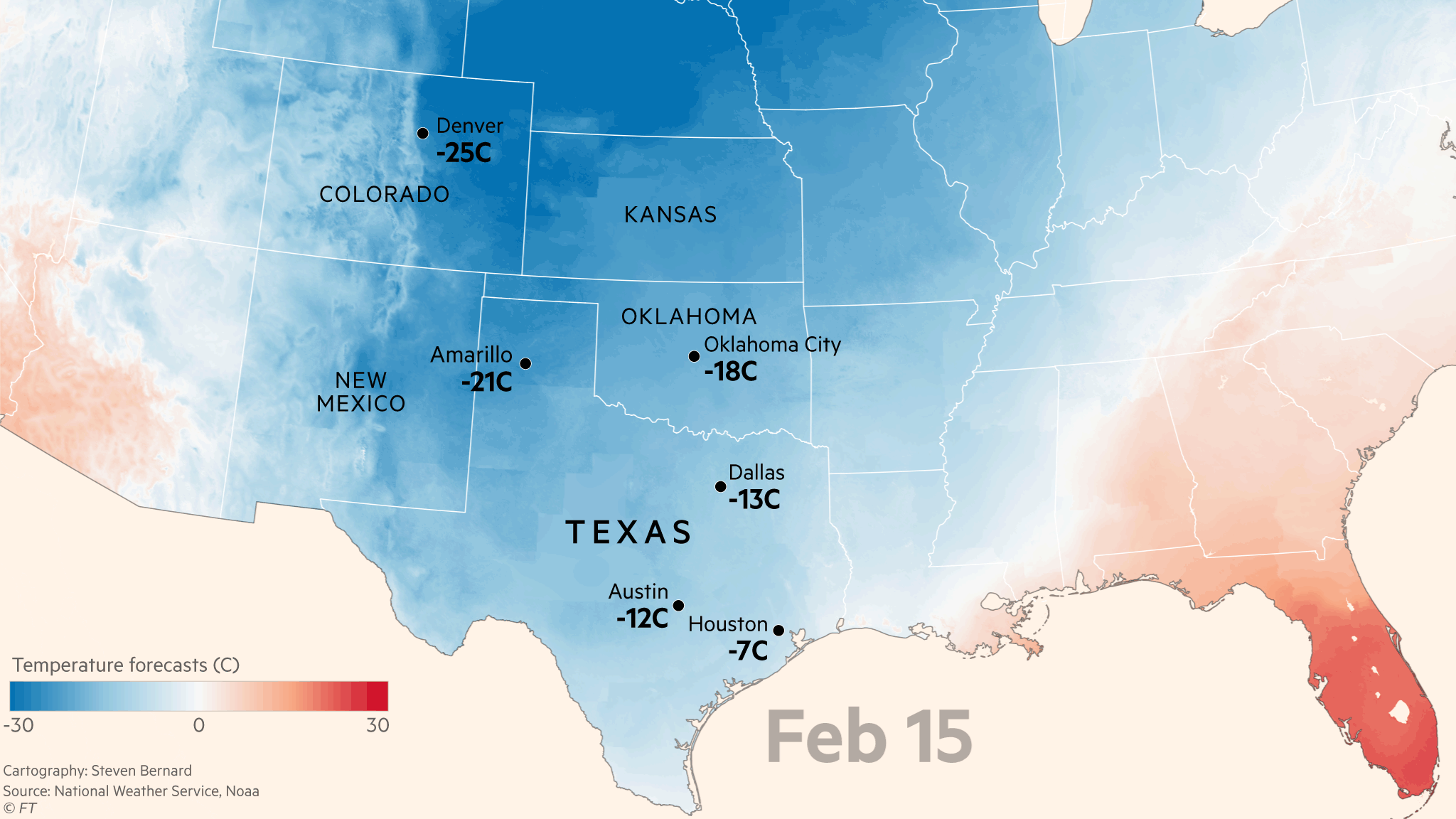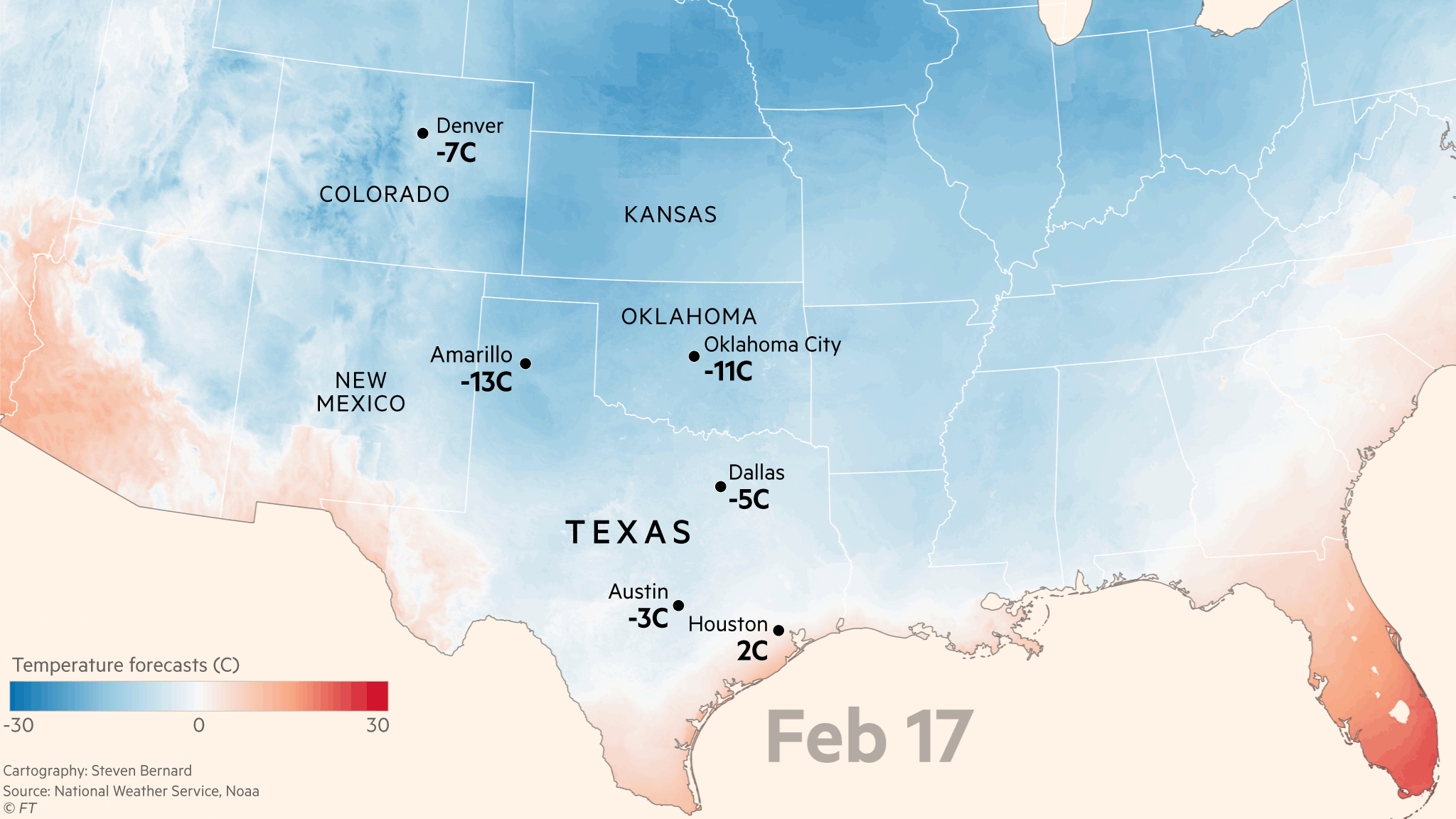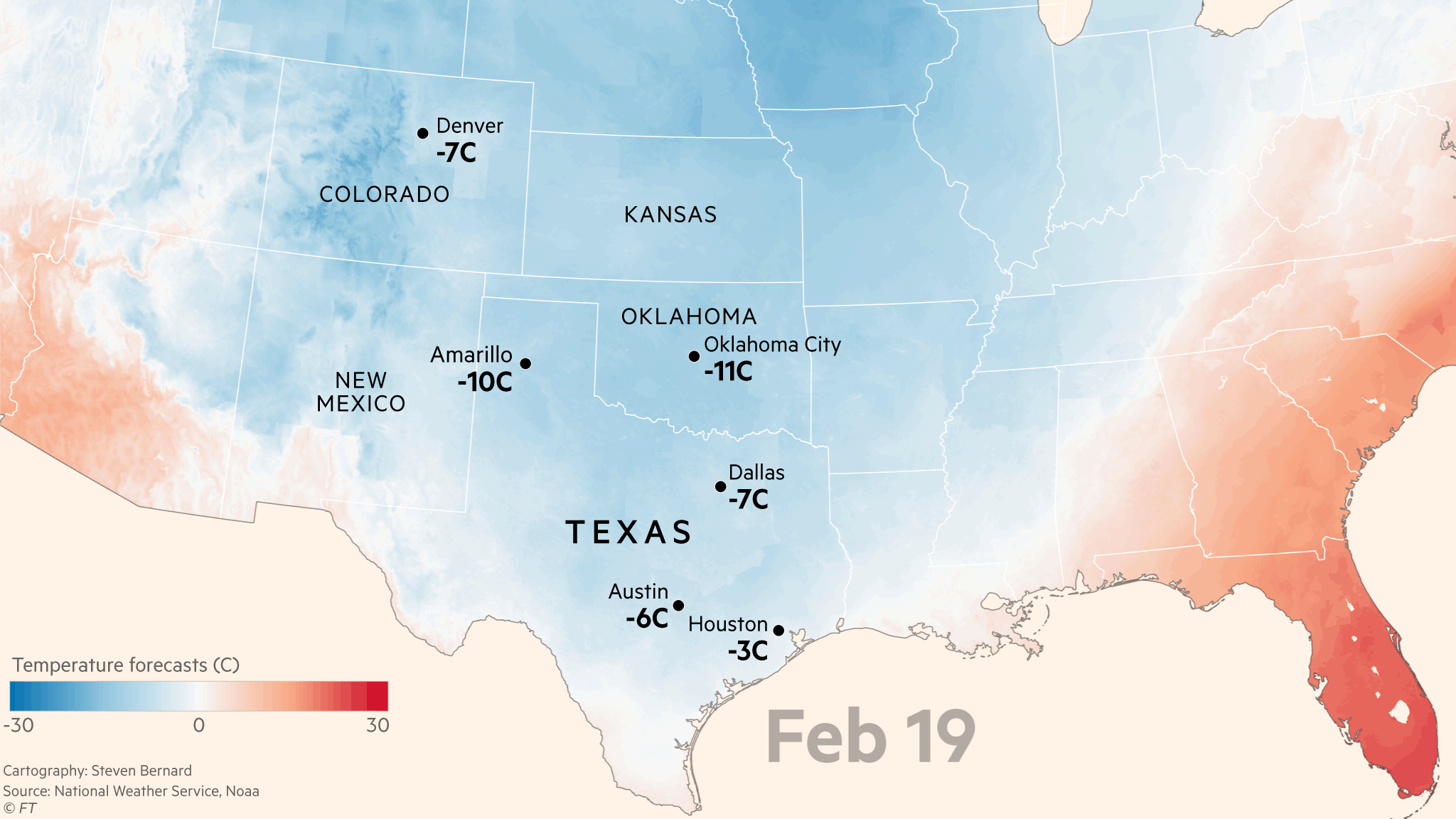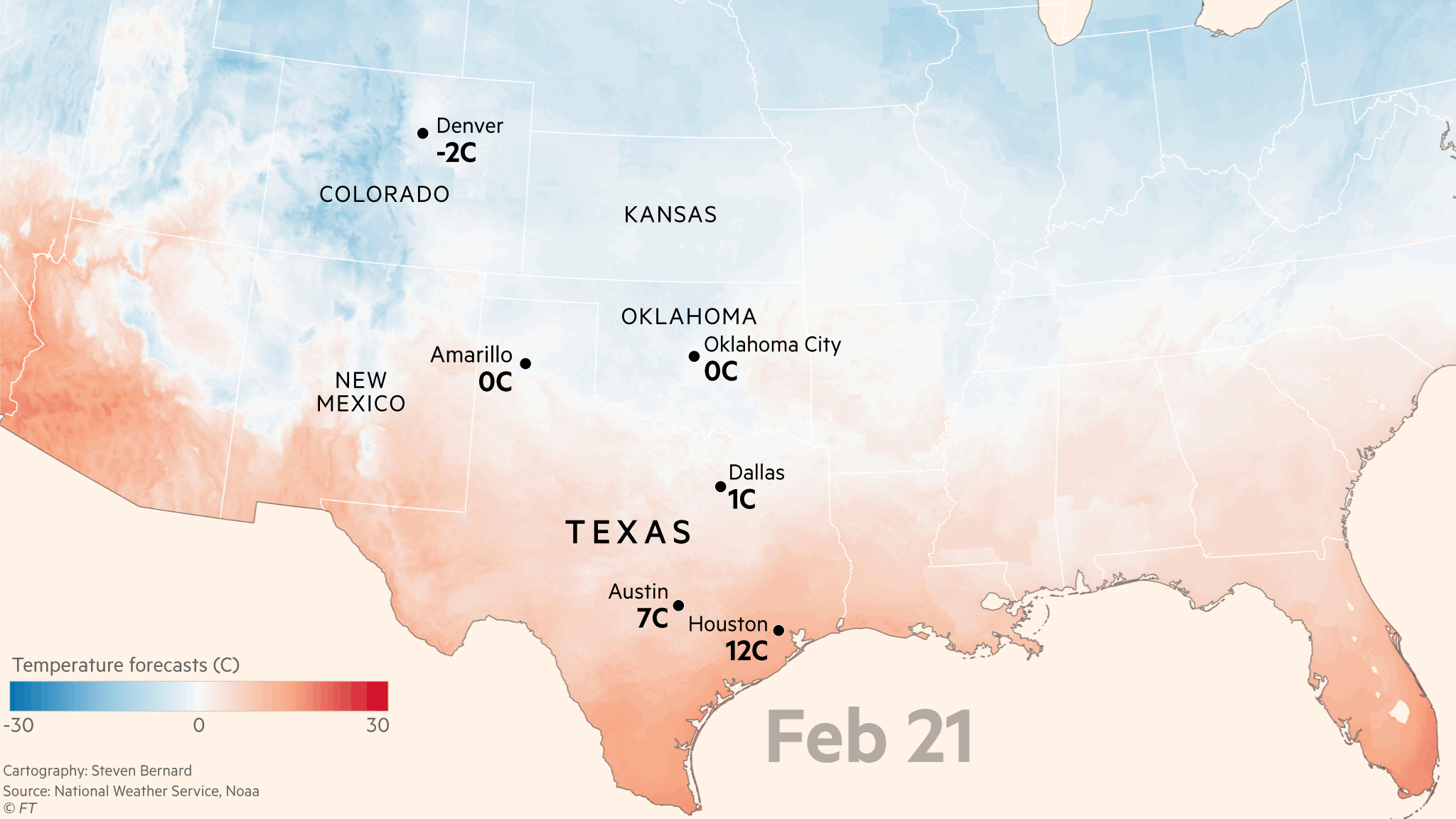
As it was stated, Electrical power generators are always scheduled for maintenance, especially before winter comes. Unfortunately, when Uri arrived, most were offline. Maintenance is needed because most homes and businesses in Texas are powered by either natural gas or electricity. (Wendorf, 2021). Because natural gas powers most in Texas, it is stored in underground chambers, which requires a pump to bring it to the surface.
Unfortunately, due to Uri’s visit to town knocking out the diesel engines responsible for the pumping, the power outage came into the picture, so some politicians in Texas were quick to point out the cause of the problem—blaming it renewable energy sources such as frozen wind turbines. However, wind turbines are not the culprit of this power outage. Although wind turbines also play a role in supporting power supply for the state, it only makes up a fraction in the reduction of power supply.
Solutions to Power Crises
White House Secretary under the Biden Administration, Jen Psaki, informed the mass that the current administration is at its foot on providing help for the affected areas and other requirements needed to surpass this issue.
Furthermore, she emphasized that the Federal Management Agency is providing power generators in the state and is also preparing to move in the diesel for other power back up to sustain the needs of its people, especially in essential infrastructures such as hospitals. Given that news circulating the state on possible longer agony of power outages, it may not suffice the needs with the current administration’s initiative. Still, at least it helps in keeping the suffering much bearable.
In addition, literally speaking, with the state’s current condition, it does not seem to be a big problem given that Texas has plenty of power available to keep up with such issue like this one. According to Dilingham, (2021), “The most recent ERCOT reports on generation adequacy indicates a reserve margin of 15.5% and increasing considerably over the next several years.” However, with the kind of unusual and rare weather conditions, not all states nor country are prepared enough to prevent such.
Despite having plenty of available resources, Texas cannot be entirely ready, especially for climate changes beyond average. As the climate changes, so are the energy planners because the climate does not only stick to a single shift, but it can also go to a series of changes that are difficult for such a state to ready entirely. Although, people can learn from this experience and possibly advance their plans. It is not necessary to be wholly perfect and sleek, but at least it can withstand for a time.
What should we do to avoid a similar disaster as the Texas Power Crisis?
With millions of people and hundreds of counties affected by power outages, we must begin extending help and not using this for political gains. Millions are experiencing loss of water and electricity, more so heat that would keep everyone warm.
This dilemma must be taken into consideration, not only by those in charge of managing such issues like this but also by civil leaders to prepare and ready for a much worse weather visit. The factual data collected and gathered about this situation are manifestations that there could be worse visits by hurricanes and winter storms in the distant future. Hence, it is essential to pay close attention to mitigate further damages and risks that may arrive.
As cited in Gavin Dillingham’s post in HARC Research Org, here are few notable recommendations for the PUCT, ERCOT, and Texas Railroad Commission, and other institutions that deal with electrical power:
1. Currently, most of Texas is an electric power island, isolated from the rest of the country. ERCOT should look seriously at interconnecting to the Eastern Connection and Western Connection.
2. Conduct a full system-wide risk assessment of climate risk threats to the power system.
3. Include climate data and modeling in energy planning, particularly in ERCOT’s Long-Term System Assessment.
4. Require all power generators and energy producers (including the natural gas system) in the state to meet minimum resilience standards.
Specific to communities, state and local leaders should require Passive Survivability — extreme weatherization of homes — to help people shelter in place in a safe environment when the power goes out, whether due to extreme heat or cold, hurricanes, floods, etc. Increasing the state’s energy efficiency resource standard (EERS) can also go a long way to ensure funding is available to do this.




